728x90
- Flowchart(흐름도): 어떠한 일을 처리하는 과정을 순서대로 간단한 기호와 도형으로 도식화한 것
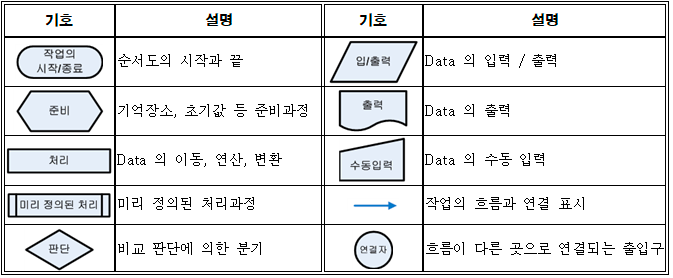
조건문
1. IF
class Control1_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char ch = 'p';
if (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') {
System.out.println("해당 문자는 영문 소문자입니다.");
} else if (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z') {
System.out.println("해당 문자는 영문 대문자입니다.");
} else {
System.out.println("해당 문자는 영문자가 아닙니다.");
}
int score = 70;
if (score >= 90) {
System.out.println("A등급입니다.");
} else if(score >= 80) {
System.out.println("B등급입니다.");
} else if(score >= 70) {
System.out.println("C등급입니다.");
}
}
}- 조건 연산자
max = ( a > b ) ? a : b;
2. SWITCH
class Control2_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int month = 8;
String monthString = "";
switch (month) {
case 1: monthString = "January";
break;
case 2: monthString = "February";
break;
case 3: monthString = "March";
break;
case 4: monthString = "April";
break;
case 5: monthString = "May";
break;
case 6: monthString = "June";
break;
case 7: monthString = "July";
break;
case 8: monthString = "August";
break;
case 9: monthString = "September";
break;
case 10: monthString = "October";
break;
case 11: monthString = "November";
break;
case 12: monthString = "December";
break;
case 0: case 13:
System.out.println("이런식으로 case 문을 사용할 수 있습니다.");
break;
case 15:
default: monthString = "Invalid month";
}
System.out.println(monthString);
}
}반복문
1. FOR
class Control3_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 초기화 시 변수 2개 사용 가능합니다. 단, 타입이 같아야 한다.
for (int i = 1, j = 10; i <= 10; i++, j--) {
System.out.println("i는 현재 " + (i) + "입니다.");
System.out.println("j는 현재 " + (j) + "입니다.");
}
System.out.println();
// 이렇게 변수 2개를 사용하여 조건식을 구성할 수 있습니다.
for (int k = 1, t = 10; k <= 10 && t > 2; k++, t--) {
System.out.println("k는 현재 " + (k) + "입니다.");
System.out.println("t는 현재 " + (t) + "입니다.");
}
}
}- 향상된 for
class Control3_5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
for (int e : arr) {
System.out.print(e + " ");
}
}
}- 임의의 정수 만들기
Math.random() : 0.0 ~ 1.0(포함x) 사이의 임의의 double 값을 반환
class Control4_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 괄호 { } 안의 내용을 20번 반복
// 1. 1 ~ 10 사이의 난수를 20개 출력하시오.
// 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10
// 2. -5 ~ 5 사이의 난수를 20개 출력하시오.
// -5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
// 1번
// System.out.println(Math.random() * 10); // 1. 0.0 * 10 <= x * 10 < 1.0 * 10
// System.out.println((int)(Math.random() * 10)); // 2. 0 <= (int)(x * 10) < 10
// System.out.println((int)(Math.random() * 10) + 1); // 3. 1 <= (int)(x * 10) + 1 < 11
// 2번
// System.out.println((int)(Math.random() * 11)); // 0 ~ 10
System.out.println((int)(Math.random() * 11) - 5); // -5 ~ 5
}
}
}
2. WHILE
class Control5_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
int i = 0;
while (sum <= 100) {
System.out.println("i = " + i);
System.out.println("sum = " + sum);
sum += ++i;
}
}
}class Control5_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int j = 1;
do {
System.out.println("do / while 문이 " + j + "번째 반복 실행중입니다.");
j++; // 이 부분을 삭제하면 무한 루프에 빠지게 됨.
} while (j < 20);
System.out.println("do / while 문이 종료된 후 변수 j의 값은 " + j + "입니다.");
}
}
- break: 자신이 포함된 하나의 반복문을 벗어남
class Control6_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
int i = 0;
while (true) {
if(sum > 100)
break;
++i;
sum += i;
}
System.out.println("i = " + i);
System.out.println("sum = " + sum);
}
}- continue: 자신이 포함된 반복문의 끝으로 이동
class Control6_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i++) {
// 3의 배수는 건너뜀 : 3, 6, 9
if (i % 3 == 0)
continue;
System.out.println("i = " + i);
}
}
}- 이름붙은 반복문: 반복문에 이름을 붙여서 하나 이상의 반복문에서 벗어남
class Control6_4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 2;
allLoop :
while (true) {
for (int j = 1; j < 10; j++) {
if (i == 5) {
break allLoop;
}
System.out.println(i + " * " + j + " = " + (i * j));
}
i++;
}
}
}class Control6_5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
allLoop : for (int i = 2; i < 10; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < 10; j++) {
if (i == 5) {
continue allLoop;
}
System.out.println(i + " * " + j + " = " + (i * j));
}
}
}
}

